Managing Myasthenia Gravis: Strategies for Treatment and Prevention

Myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disorder, typically emerges later in life due to antibodies attacking muscle receptors, hindering essential chemical signals for muscle contraction. Its symptoms range from visual disturbances like drooping eyelids and double vision to muscle weakness and fatigue, often exacerbating with muscle use. Diagnosis relies on medical history, physical exams, and tests like blood tests and electromyograms to assess muscle activity.
Managing Multiple System Atrophy (MSA): Challenges and Treatment

Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized by diverse symptoms, often leading to initial misdiagnosis as idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis relies heavily on clinical features, particularly autonomic dysfunction like orthostatic hypotension. Management aims at symptom relief through both pharmacologic therapies for movement disorders and orthostatic hypotension, alongside nonpharmacologic interventions such as dietary adjustments and therapies like physical and speech therapy.
Understanding and Managing Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP)

Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by movement, balance, speech, swallowing, and eye movement difficulties, alongside other symptoms. It presents with various clinical variants linked to tau protein accumulation and neuronal loss in specific brain regions. Despite symptom variability, PSP consistently exhibits tau pathology and is classified among atypical Parkinsonian syndromes, causing significant physical and cognitive impairments that can lead to heightened mortality without proper management.
NORD: Enhancing Care, Advancing Research, and Empowering the Rare Disease Community
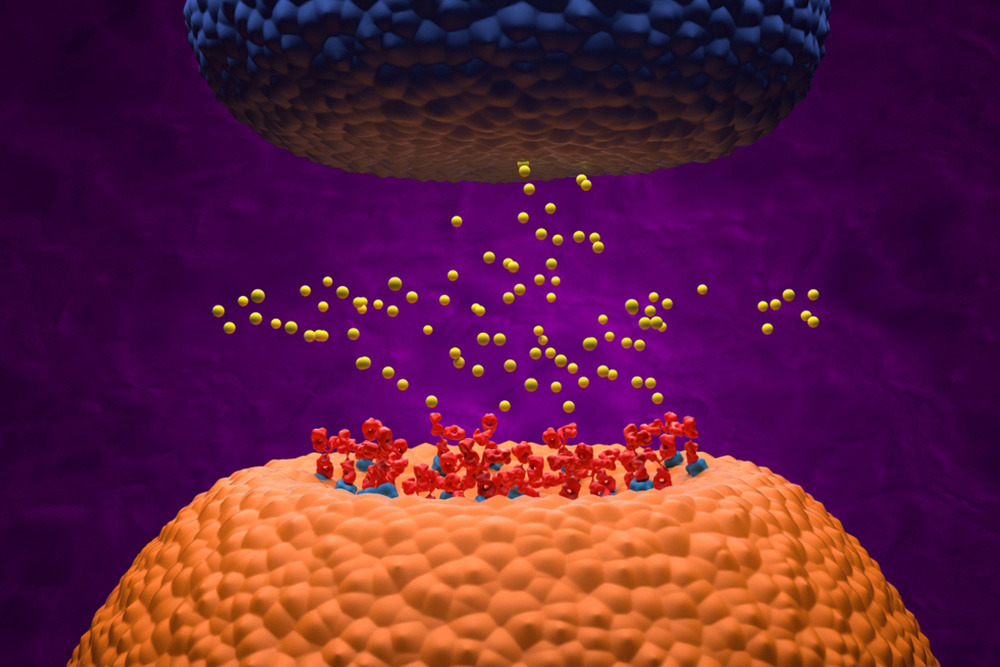
Myasthenia gravis (MG), an autoimmune disorder affecting neuromuscular junctions, has seen significant advancements in treatment since the introduction of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in 1934, which dramatically improved patient outcomes. Despite these advances, managing MG can be complex, particularly with treatment-refractory cases that lead to recurrent hospitalizations and necessitate ongoing interventions like IVIG or plasma exchange.
Comprehensive Management of Stiff Person Syndrome: From Diagnosis to Treatment Options

Stiff person syndrome (SPS) is a rare autoimmune disorder of the central nervous system. It features progressive muscle rigidity and spasms, primarily affecting the axial and proximal limb muscles, and is associated with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (anti-GAD) antibodies, linking it to other autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes and thyroid disease. The disorder can lead to severe disability and increased mortality if untreated and presents in various forms, including classic SPS, partial variants, and the severe progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity and myoclonus (PERM).
Understanding Myasthenia Gravis: Advances in Treatment and Management

Stiff person syndrome (SPS) is a rare autoimmune disorder of the central nervous system. It features progressive muscle rigidity and spasms, primarily affecting the axial and proximal limb muscles, and is associated with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (anti-GAD) antibodies, linking it to other autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes and thyroid disease. The disorder can lead to severe disability and increased mortality if untreated and presents in various forms, including classic SPS, partial variants, and the severe progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity and myoclonus (PERM).

